April 13, 2021 | Vanessa McMains
So-called ‘magic mushroom’ drug seems to work through multiple brain mechanisms for its different effects
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers have shown that psilocybin—the active chemical in “magic mushrooms”— still works its antidepressant-like actions, at least in mice, even when the psychedelic experience is blocked. The new findings, published this week in PNAS, suggest that psychedelic drugs work in multiple ways in the brain, and it may be possible to deliver the fast-acting antidepressant therapeutic benefit without requiring daylong guided-therapy sessions. A version of the drug without, or with less of, the psychedelic effects could loosen restrictions on who could receive the therapy and lower costs, making the benefits of psilocybin more available to more people in need.
In all clinical trials performed to date, the person treated with psilocybin remains under the care of a guide, who keeps the person calm and reassures them during their daylong experience. This can include hallucinations, altered perception of time and space, and intense emotional and spiritual encounters.
Researchers in the field have long attributed psilocybin’s effectiveness to the intense psychedelic experience.
 “We do not understand the mechanisms that underlie the antidepressant actions of psilocybin and the role that the profound psychedelic experience during these sessions plays in the therapeutic benefits,” says Scott Thompson, Ph.D., Professor and Chair, Department of Physiology at UMSOM and senior author of the study. “The psychedelic experience is incredibly powerful and can be life-changing, but that could be too much for some people or not appropriate.”
“We do not understand the mechanisms that underlie the antidepressant actions of psilocybin and the role that the profound psychedelic experience during these sessions plays in the therapeutic benefits,” says Scott Thompson, Ph.D., Professor and Chair, Department of Physiology at UMSOM and senior author of the study. “The psychedelic experience is incredibly powerful and can be life-changing, but that could be too much for some people or not appropriate.”
Several barriers prevent the widespread use of psychedelic compounds. For example, there is fear that the psychedelic experience may promote psychosis in people who are predisposed to severe mental disorders, like bipolar disorder and schizophrenia, so the clinical therapy sessions performed to date have been limited to a highly selected screened group without a family history of these disorders.
Dr. Thompson adds that there may also be an equity issue, because not everyone can take several days off work to prepare and engage in the experience. The costs of staffing a facility with at least one trained guide per treated person per day and a private space may also be prohibitive to all but a few. He says it is conceivable that a depression treatment derived from psilocybin could be developed without the psychedelic effects, so people can take it safely at home without requiring a full day in a care facility.
For their study, led by UMSOM MD/PhD student Natalie Hesselgrave, the team used a mouse model of depression in which mice were stressed for several hours a day over 2-3 weeks. Because researchers cannot measure mouse moods, they measure their ability to work for rewards, such as choosing to drink sugar water over plain water. People suffering from depression lose the feeling of pleasure for rewarding events. Similarly, stressed mice no longer preferred sugar water over plain water. However, 24 hours after a dose of psilocybin, the stressed mice regained their preference for the sugar water, demonstrating that the drug restored the mice’s pleasure response.
Psilocybin exerts its effects in people by binding to and turning on receptors for the chemical messenger serotonin. One of these receptors, the serotonin 2A receptor, is known to be responsible for the psychedelic response. To see if the psychedelic effects of psilocybin were needed for the anti-depressive benefits, the researchers treated the stressed mice with psilocybin together with a drug, ketanserin, which binds to the serotonin 2A receptor and keeps it from being turned on. The researchers found that the stressed mice regained their preference for the sugar water in response to psilocybin, even without the activation of the psychedelic receptor.
“These findings show that activation of the receptor causing the psychedelic effect isn’t absolutely required for the antidepressant benefits, at least in mice,” says Dr. Thompson, “but the same experiment needs to be performed in depressed human subjects.” He says his team plans to investigate which of the 13 other serotonin receptors are the ones responsible for the antidepressant actions.
“This new study has interesting implications, and shows that more basic research is needed in animals to reveal the mechanisms for how these drugs work, so that treatments for these devastating disorders can be developed,” says E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, University of Maryland Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, University of Maryland School of Medicine.
This work was funded by the National Institute of Mental Health (R01 MH086828) and the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (T32 GM092237).
Although not approved yet, Dr. Thompson and the University of Maryland Baltimore have filed a patent on using psilocybin with drugs that block serotonin 2A receptors to treat depression.
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has nearly $600 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The combined School of Medicine and Medical System (“University of Maryland Medicine”) has an annual budget of over $6 billion and an economic impact of nearly $20 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2021, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #9 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 15 percent (#27) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu
Contact
Vanessa McMains
Director, Media and Public Affairs
443-875-6099
vmcmains@ihv.umaryland.edu
Related stories

Wednesday, March 27, 2019
UMSOM Researchers Discover a Critical Receptor Involved in the Response to Fast-Acting Antidepressants Like Ketamine
Effective treatment of clinical depression remains a major mental health issue, with roughly 30 percent of patients who do not respond to any of the available treatments. Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have discovered a crucial receptor called mGlu2 that is critical to the mechanism of fast-acting antidepressants such as ketamine when used to treat depression.
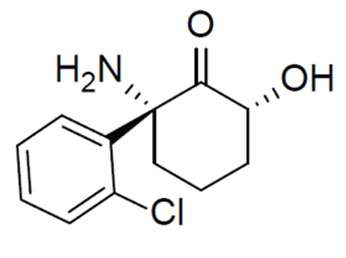
Wednesday, May 04, 2016
UM SOM Researchers Identify Potentially Revolutionary Antidepressant Compound
For years, scientists and doctors have known that ketamine can treat depression very rapidly, often working within hours, compared to weeks or months for widely used antidepressants. However, the drug, which is approved as an anesthetic, has major side effects – it is linked to hallucinations and dissociation - a sense of being outside your own body – and for these reasons is abused as a club drug. Not surprisingly, this limits its use in the treatment of depression.
