July 07, 2021 | Deborah Kotz
Tests Can Accurately Detect Virus in Minutes Using Nanoparticle and Electrochemical Sensing Techniques
 Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have developed two rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 that are nearly as accurate as the gold-standard test currently used in laboratories. Unlike the gold-standard test, which extracts RNA and uses it to amplify the DNA of the virus, these new tests can detect the presence of the virus in as little as five minutes using different methods.
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have developed two rapid diagnostic tests for COVID-19 that are nearly as accurate as the gold-standard test currently used in laboratories. Unlike the gold-standard test, which extracts RNA and uses it to amplify the DNA of the virus, these new tests can detect the presence of the virus in as little as five minutes using different methods.
One test is a COVID-19 molecular diagnostic test, called Antisense, that uses electrochemical sensing to detect the presence of the virus. The other uses a simple assay of gold nanoparticles to detect a color change when the virus is present. Both tests were developed by Dipanjan Pan, PhD, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Nuclear Medicine and Pediatrics at UMSOM and his research team. Dr. Pan has a joint appointment at the University of Maryland Baltimore County (UMBC).
“These tests detect the presence of the virus within 5 to 10 minutes and rely on simple processes that can be performed with little lab training,” said Dr. Pan. They do not require the extraction of the virus’s RNA, which is both complicated and time consuming.
They also are more reliable than the rapid antigen tests currently on the market, which detect the virus only in those with significantly high viral levels. “These two newer tests are extremely sensitive and can detect the presence of the virus, even in those with low levels of the virus,” Dr. Pan said.
 Dr. Pan's team included UMSOM research fellow Maha Alafeef, UMSOM research associate Parikshit Moitra, PhD, and research fellow Ketan Dighe, from UMBC.
Dr. Pan's team included UMSOM research fellow Maha Alafeef, UMSOM research associate Parikshit Moitra, PhD, and research fellow Ketan Dighe, from UMBC.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) registered the laboratory of Dr. Pan as an approved laboratory development site for the Antisense test in June. The move paves the way for Dr. Pan’s laboratory to begin conducting the test at the university, in research settings, as it undergoes further development.
In February, RNA Disease Diagnostics, Inc. (RNADD) received an exclusive global license from UMB and UMBC to commercialize the test. Dr. Pan serves as an unpaid scientific advisor to the company.
This test detects the virus in a swab sample using an innovative technology called electrochemical sensing. It uses a unique dual-pronged molecular detection approach that integrates electrochemical sensing to rapidly detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus. “The final prototype is like a glucometer, which patients with diabetes use at home to measure their blood glucose levels,” said Dr. Pan, “and is just as easy for people to do themselves.”
Dr. Pan and his colleagues, in collaboration with RNA Disease Diagnostics, are launching a study of NBA basketball players in New York City to compare the Antisense test to rapid COVID tests that the NBA is using to monitor COVID infections in its players.
“We would like to see whether our test can yield more reliable results compared to the existing platforms,” he said. “Current antigen-based rapid COVID tests miss infections about 20 percent of the time and also have high rates of false positive results. Our Antisense test appears to be about 98 percent reliable, which is similar to the PCR test.”
Similar to the Antisense test, the second rapid test also does not require the use of any advanced laboratory techniques, such as those commonly used to extract RNA, for analysis. It uses a simple assay containing plasmonic gold nanoparticles to detect a color change when the virus is present. In April, Dr. Pan and his colleagues published a stepwise protocol in the journal Nature Protocols, explaining how the nano-amplified colorimetric test works and how it can be used.
Once a nasal swab or saliva sample is obtained from a patient, the nucleic acid (bits of genetic material) in the sample is amplified via a simple process that takes about 10 minutes. The test uses a highly specific molecule attached to the gold nanoparticles to detect a particular protein. This protein is part of the genetic sequence that is unique to the novel coronavirus. When the biosensor binds to the virus’ gene sequence, the gold nanoparticles respond by turning the liquid reagent from purple to blue.
“Innovations in COVID-19 testing remain incredibly important even as the epidemic appears to be waning in this country,” said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, UM Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “As we continue to monitor infections in unvaccinated segments of our population and the potential spread of new variants, there will be a vital need for inexpensive rapid tests to ensure that we continue to maintain low infection rates.”
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has nearly $600 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The combined School of Medicine and Medical System (“University of Maryland Medicine”) has an annual budget of over $6 billion and an economic impact of nearly $20 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2021, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #9 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 15 percent (#27) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu
Contact
Deborah Kotz
410-706-4255
dkotz@som.umaryland.edu
Related stories

Tuesday, December 20, 2022
COVID Vaccines Prevented 3 Million Deaths in the U.S., New Analysis Finds
In the two years since the first COVID-19 vaccines were given to patients in the U.S., the vaccines had the cumulative effect of preventing 18 million hospitalizations and 3 million deaths. That is based on a new modeling analysis conducted by a researcher at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and her colleagues. Results of the analysis were published by the Commonwealth Fund.

Wednesday, February 16, 2022
Study Shows New Drug Combination More Effective Against SARS-CoV-2
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine have identified a powerful combination of antivirals to treat COVID-19. The researchers showed that combining the experimental drug brequinar with either of the two drugs already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for emergency use, remdesivir or molnupiravir, inhibited growth of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in human lung cells and in mice. Their findings suggest that these drugs are more potent when used in combination than individually.

Wednesday, January 26, 2022
Trial Co-led by University of Maryland School of Medicine Scientist Confirms Safety of “Mix-and-Match” COVID-19 Vaccine Booster Dosing
A University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD), expert is co-leading an ongoing study that was pivotal in recommending adults and teens receive booster COVID-19 shots of their choosing starting in fall 2021. The preliminary clinical trial results, reported today in The New England Journal of Medicine, found that is safe and effective to receive boosters that are the same or a different one from the person’s primary vaccine(s).

Thursday, December 16, 2021
Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine Found to be Safe and Effective in Phase 3 Trial Conducted by UM School of Medicine Researchers
An investigational COVID-19 vaccine made by Novavax was found to be 90 percent effective at preventing COVID-19 illness, according to results from a Phase 3 clinical trial published today in the New England Journal of Medicine. The University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM) Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health served as one of the trial sites, and Karen Kotloff, MD, Professor of Pediatrics at UMSOM, served as Co-Chair for the trial protocol.

Tuesday, December 14, 2021
UM School of Medicine’s Office of Public Affairs and Communications Honored with 2021 PRSA ‘Best In Maryland’ Award
The University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM)'s Office of Public Affairs & Communications received the Public Relations Society of America (PRSA) 2021 “Best in Maryland Award,” the PRSA’s highest honor, for its COVID-19 Communications program. The award was given at the PRSA Maryland Gala, held on December 9, 2021.

Wednesday, September 08, 2021
UM School of Medicine Reaching Underserved Communities Through Grass Roots Efforts to Increase COVID-19 Vaccination Rates
In an effort to increase COVID-19 vaccination rates among children and families, and ultimately help bring the pandemic under control, the Department of Family & Community Medicine (DFCM) and the Department of Psychiatry at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) are partnering with key community and faith-based groups in Baltimore city to reach the most vulnerable and underserved communities. This partnership will also extend across Maryland, Delaware, Virginia, and West Virginia.

Wednesday, June 09, 2021
Global Study of Microbes in 60 Cities Finds Each Has Unique Fingerprint of Viruses and Bacteria
Each city has its own unique microbiome, a “fingerprint” of viruses and bacteria that serves as type of city profile, according to a new study from an international consortium of researchers that included a team from the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM). The international project, which sequenced and analyzed samples collected from public transit systems and hospitals in 60 cities around the world, was published today in the journal Cell.

Tuesday, March 16, 2021
New Study Finds Healthcare Settings Do Not Pose Added Risk Factor for Covid-19 Infection Spread Among U.S. Healthcare Personnel
Healthcare personnel who were infected with COVID-19 faced stronger risk factors outside of the workplace than in their hospital or healthcare settings. That is the finding of a new study published today in the Journal of the American Medical association's JAMA Network Open conducted by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers and colleagues at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and three other universities.

Thursday, January 21, 2021
UM School of Medicine Hosted Media Availability for Ensuring Trust in COVID-19 Vaccine Event
On January 22, 2021 at 2 p.m., the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) hosted Black faith-based leaders, COVID-19 research volunteers, and “America’s Doctor,” Anthony Fauci, MD. The event provided straight talk about fears, trust issues, and why we need our Black and Brown community to be a part of COVID-19 vaccine research.
Tuesday, January 05, 2021
Dr. Kathleen Neuzil, World-renowned Leader in Vaccine Research, Receives Moderna Vaccine
Kathleen Neuzil, MD, MPH, FIDSA, the Myron M. Levine, MD, DTPH, Professor of Vaccinology and Director of the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM)’s Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD), received her first injection of the Moderna vaccine for COVID-19 on December 31. Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) played an integral part in the dedicated work that led to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issuing an Emergency Use Authorization for the Moderna vaccine in December.

Tuesday, January 05, 2021
University of Maryland School of Medicine Begins Phase 3 Trial of Novavax COVID-19 Vaccine Candidate
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) will participate in a Phase 3 clinical trial of an investigational COVID-19 vaccine to protect against SARS-CoV-2, the coronavirus causing COVID-19 that continues to impact millions of people around the world. The clinical trial will test the safety and effectiveness of NVX-CoV2373, being developed by U.S. biotechnology company, Novavax, Inc., based in Gaithersburg, MD.

Thursday, November 19, 2020
Promising Results Seen in Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 Vaccine After Phase 1 Trial by University of Maryland School of Medicine
Just six months after beginning a clinical development program that first enrolled here at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), Pfizer and BioNTech report interim results showing an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine had no serious safety concerns and has been found to be 95 percent effective in protecting individuals from COVID-19.

Friday, November 13, 2020
UM School of Medicine and School of Pharmacy Researchers Identify Promising New Compounds to Potentially Treat Novel Coronaviruses
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and School of Pharmacy (UMSOP) have discovered new drug compounds to potentially treat the novel coronavirus that causes COVID-19. The compounds disrupt the functioning of a protein complex inside human cells that the researchers discovered is critical for the replication and survival of coronaviruses. This finding could lead to the development of new broad-spectrum antiviral drugs that target viruses such as influenza, Ebola and coronaviruses, according to a new study published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) journal.
Tuesday, June 16, 2020
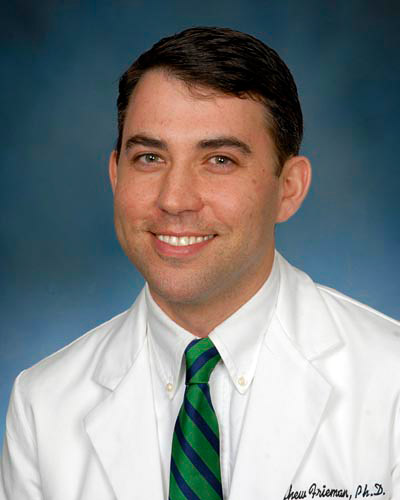
UM School of Medicine Researchers Receive Federal Funding to Rapidly Test New Treatments for COVID-19
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) will be partnering on an agreement funded by the federal government’s Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to rapidly test hundreds of drugs, approved and marketed for other conditions, to see whether any can be repurposed to prevent or treat COVID-19. The compounds will be tested in studies using state-of-the-art technologies in the laboratory of coronavirus researcher Matthew Frieman, PhD., Associate Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine. UMSOM will receive up to $3.6 million over the next year to fund this effort.

Tuesday, June 02, 2020
UM School of Medicine’s Institute of Human Virology Awarded Grants to Strengthen COVID-19 Response in Sub-Saharan Africa
The Center for International Health, Education and Biosecurity (Ciheb) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s Institute of Human Virology was awarded $4 million from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to support coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) response activities in Botswana, Nigeria, Malawi, and Mozambique.
Monday, June 01, 2020
In A COVID-19 World, Another Threat to the Health of Our Children
In the U.S., our children rarely fall ill to grave infections because they are protected by vaccines. Serious illnesses like measles, mumps, congenital rubella syndrome, chickenpox, diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, rotavirus diarrhea, hepatitis (A and B), polio and bacterial meningitis are all preventable through routine childhood vaccinations.

Thursday, May 28, 2020
UM School of Medicine Researchers Develop Experimental Rapid COVID-19 Test Using Innovative Nanoparticle Technique
Scientists from the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) developed an experimental diagnostic test for COVID-19 that can visually detect the presence of the virus in 10 minutes. It uses a simple assay containing plasmonic gold nanoparticles to detect a color change when the virus is present. The test does not require the use of any advanced laboratory techniques, such as those commonly used to amplify DNA, for analysis. The authors published their work last week in the American Chemical Society’s nanotechnology journal ACS Nano.

Thursday, May 21, 2020
UM School of Medicine Begins First Innovative Trial of Experimental Stem Cell Therapy to Reduce Deaths in Sickest COVID-19 Patients
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have begun testing an experimental stem cell therapy developed by Mesoblast Limited to treat hospitalized COVID-19 patients with moderate to severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) who are on ventilators to help them breathe. The trial, which is being conducted at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC) and additional sites across the U.S, will involve a total of 300 patients randomized to receive either the drug remestemcel-L or a placebo in addition to the recommended standard of care to manage severe COVID-19 infections. The first patient in this national trial was treated at UMMC.
Tuesday, May 05, 2020
UM School of Medicine is First in U.S. to Test Unique RNA Vaccine Candidate for COVID-19
In a significant development in the global effort to discover a safe and effective vaccine for COVID-19, researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) became the first in the U.S. to begin testing experimental COVID-19 vaccine candidates developed by Pfizer and BioNTech. The research, funded by Pfizer Inc., will study the safety, efficacy, and dosing of an experimental mRNA -based vaccine.

Thursday, April 23, 2020
UM School of Medicine Researchers Test Remdesivir as Potential Therapy for COVID-19 Patients
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) are testing the effectiveness of the investigational antiviral drug remdesivir in hospitalized adult patients with SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). The randomized controlled clinical trial is evaluating the safety and effectiveness of the drug, and it is part of a national study funded by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).

Friday, April 10, 2020
University of Maryland School of Medicine Launches New Large Scale COVID-19 Testing Initiative
University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, announced today the launch of a large-scale COVID-19 Testing Initiative that will significantly expand testing capability over the coming weeks, enabled by new funding of $2.5 million from the State of Maryland.