February 05, 2021 | Deborah Kotz
UMSOM Uniquely Positioned to Link Basic Science Research to Clinical Trials.
 Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have found promising results in pre-clinical studies for a new experimental vaccine against COVID-19 made by Novavax. The vaccine was found to generate a robust immune response in animals exposed to the vaccine with strong data indicating safety and efficacy, according to the study published recently in the journal Nature Communications. The results have been used to begin testing the vaccine in human trials in the U.S. with a Phase 3 trial that recently launched at the UMSOM’s Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health.
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have found promising results in pre-clinical studies for a new experimental vaccine against COVID-19 made by Novavax. The vaccine was found to generate a robust immune response in animals exposed to the vaccine with strong data indicating safety and efficacy, according to the study published recently in the journal Nature Communications. The results have been used to begin testing the vaccine in human trials in the U.S. with a Phase 3 trial that recently launched at the UMSOM’s Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health.
The vaccine is a stable protein that is manufactured from the genetic sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus spike protein. As with traditional vaccines like the flu shot, the Novavax vaccine uses adjuvants to boost the immune response in those who receive it.
“We found this vaccine produces high antibody levels leading to significant protection from SARS-CoV-2 in mice. Together with the non-human primate data, this suggests that the vaccine will be highly protective in humans. Our previous work, with Novavax on a MERS coronavirus vaccine and now SARS-CoV-2, demonstrates that continued support of basic science is essential in the response to pandemics,” said study co-author Matthew Frieman, PhD, Associate Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at UMSOM.
The vaccine trial is being conducted by researchers in UMSOM’s Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD) as part of their National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases-funded Vaccine Treatment and Evaluation Unit (VTEU), and the COVID-19 Prevention Network (CoVPN). It adds to the extensive COVID-19 vaccine research that has been underway on campus since early spring. The UMSOM site is in the process of recruiting up to 500 participants out of 30,000 total who will take part in the trial. The aim is to include diverse populations most impacted by COVID-19. They will include people who have increased risk of exposure because of location or circumstance, such as occupation. Individuals 65 and older, African Americans and LatinX populations, as well as individuals at risk of severe COVID-19, will be represented.
The Novavax vaccine candidate, NVX-CoV2373, is a stabilized, prefusion protein antigen derived from the genetic sequence of the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus spike (S) protein and is formulated with Novavax’s proprietary adjuvant Matrix‑M™. NVX-CoV2373 contains purified protein antigen and can neither replicate nor can it cause COVID-19.
The vaccine has been in Phase 3 trials in the U.K., with more than 15,000 participants enrolled. Interim data in this event-driven trial are expected as soon as early first quarter of 2021.
 “Our coronavirus experts at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have been at the forefront of basic research efforts that have helped develop new treatments and vaccines against COVID-19,” said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, UM Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “For this new vaccine made by Novavax, our researchers have worked on every aspect of its development from bench studies to Phase 3 clinical trials. It speaks to the broad expertise and collaborative efforts of our faculty. This latest research will lead us a step closer to providing another potentially lifesaving tool in the vaccine arsenal.”
“Our coronavirus experts at the University of Maryland School of Medicine have been at the forefront of basic research efforts that have helped develop new treatments and vaccines against COVID-19,” said E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, Executive Vice President for Medical Affairs, UM Baltimore, and the John Z. and Akiko K. Bowers Distinguished Professor and Dean, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “For this new vaccine made by Novavax, our researchers have worked on every aspect of its development from bench studies to Phase 3 clinical trials. It speaks to the broad expertise and collaborative efforts of our faculty. This latest research will lead us a step closer to providing another potentially lifesaving tool in the vaccine arsenal.”
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
Now in its third century, the University of Maryland School of Medicine was chartered in 1807 as the first public medical school in the United States. It continues today as one of the fastest growing, top-tier biomedical research enterprises in the world -- with 46 academic departments, centers, institutes, and programs, and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians, scientists, and allied health professionals, including members of the National Academy of Medicine and the National Academy of Sciences, and a distinguished two-time winner of the Albert E. Lasker Award in Medical Research. With an operating budget of more than $1.2 billion, the School of Medicine works closely in partnership with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide research-intensive, academic and clinically based care for nearly 2 million patients each year. The School of Medicine has nearly $600 million in extramural funding, with most of its academic departments highly ranked among all medical schools in the nation in research funding. As one of the seven professional schools that make up the University of Maryland, Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine has a total population of nearly 9,000 faculty and staff, including 2,500 students, trainees, residents, and fellows. The combined School of Medicine and Medical System (“University of Maryland Medicine”) has an annual budget of over $6 billion and an economic impact of nearly $20 billion on the state and local community. The School of Medicine, which ranks as the 8th highest among public medical schools in research productivity (according to the Association of American Medical Colleges profile) is an innovator in translational medicine, with 606 active patents and 52 start-up companies. In the latest U.S. News & World Report ranking of the Best Medical Schools, published in 2021, the UM School of Medicine is ranked #9 among the 92 public medical schools in the U.S., and in the top 15 percent (#27) of all 192 public and private U.S. medical schools. The School of Medicine works locally, nationally, and globally, with research and treatment facilities in 36 countries around the world. Visit medschool.umaryland.edu
Contact
Deborah Kotz
410-706-4255
dkotz@som.umaryland.edu
Related stories

Thursday, March 28, 2024
NIH selects Dr. Kathleen Neuzil as Director of The Fogarty International Center
Kathleen M. Neuzil, MD, MPH, Director of the University of Maryland School of Medicine’s (UMSOM) Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health, has been named the 13th director of the Fogarty International Center (FIC), which is part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Dr. Neuzil will be the first woman to hold the permanent directorship since the center’s founding in 1968 and will also hold the position of Associate Director for International Research at NIH.

Tuesday, December 20, 2022
COVID Vaccines Prevented 3 Million Deaths in the U.S., New Analysis Finds
In the two years since the first COVID-19 vaccines were given to patients in the U.S., the vaccines had the cumulative effect of preventing 18 million hospitalizations and 3 million deaths. That is based on a new modeling analysis conducted by a researcher at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and her colleagues. Results of the analysis were published by the Commonwealth Fund.

Friday, October 07, 2022
Other SARS-CoV-2 Proteins are Important for Disease Severity, Aside from the Spike
University of Maryland School of Medicine researchers have identified how multiple genes of SARS-CoV-2 affect disease severity, which could lead to new ways in how we develop future vaccines or develop newer treatments. The genes control the immune system of the host, contributing to how fiercely the body responds to a COVID-19 infection.

Wednesday, February 16, 2022
Study Shows New Drug Combination More Effective Against SARS-CoV-2
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine have identified a powerful combination of antivirals to treat COVID-19. The researchers showed that combining the experimental drug brequinar with either of the two drugs already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for emergency use, remdesivir or molnupiravir, inhibited growth of the SARS-CoV-2 virus in human lung cells and in mice. Their findings suggest that these drugs are more potent when used in combination than individually.
Tuesday, June 16, 2020
UM School of Medicine Researchers Receive Federal Funding to Rapidly Test New Treatments for COVID-19
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) will be partnering on an agreement funded by the federal government’s Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) to rapidly test hundreds of drugs, approved and marketed for other conditions, to see whether any can be repurposed to prevent or treat COVID-19. The compounds will be tested in studies using state-of-the-art technologies in the laboratory of coronavirus researcher Matthew Frieman, PhD., Associate Professor of Microbiology and Immunology at the University of Maryland School of Medicine. UMSOM will receive up to $3.6 million over the next year to fund this effort.

Monday, June 15, 2020
UM School of Medicine Researchers Help Identify Potent Antibody Cocktail with Potential to Treat COVID-19
Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) evaluated several human antibodies to determine the most potent combination to be mixed in a cocktail and used as a promising anti-viral therapy against the virus that causes COVID-19. Their research, conducted in collaboration with scientists at Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, was published today in the journal Science. The study demonstrates the rapid process of isolating, testing and mass-producing antibody therapies against any infectious disease by using both genetically engineered mice and plasma from recovered COVID-19 patients.

Tuesday, December 10, 2019
UMSOM Researchers to Test Vaccine Designed to Protect Against Serious Illness from Contaminated Food and Water
Each year, millions of people contract serious diarrheal illnesses typically from contaminated food and water. Among the biggest causes of diarrheal diseases are the bacteria Shigella and enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC), and researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine are testing a vaccine designed to offer protection against these serious pathogens.
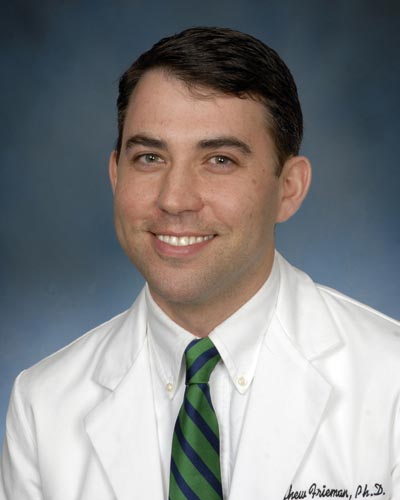

Friday, October 18, 2019
Diabetes Worsens Respiratory Illness Due to Abnormal Immune Response, UM School of Medicine Study Finds
Since the Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) first emerged in Saudi Arabia in 2012, there have been more than 2,400 confirmed cases of the infection, resulting in greater than 800 deaths – an alarming fatality rate of 35 percent. For this reason, researchers have been eager to identify any risk factors that contribute to the development of severe or lethal disease. Current clinical evidence points to diabetes as a major risk factor in addition to other comorbidities including kidney disease, heart disease, and lung disease.
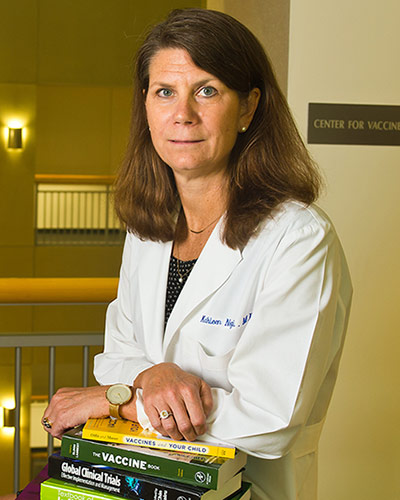

Friday, September 20, 2019
UM School of Medicine's Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health Receives NIH Contract of up to More than $200 Million for Influenza Research
Kathleen Neuzil, MD, MPH, Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics and Director of the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) and Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, announced that CVD has been awarded a contract from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), with total funding up to more than $200 million over seven years if all contract options are exercised.
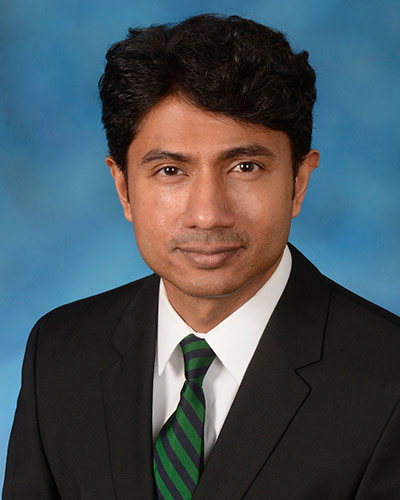

Monday, August 19, 2019
UM School of Medicine Researcher Warns of Need for Malaria Drug to Treat Severe Cases in U.S.
Each year there are more than 200 million cases of malaria worldwide, a mosquito-borne disease caused by a parasite that brings on fever and body aches and, in some cases, more serious conditions such as coma and death. While the vast majority of these cases occur in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, the U.S. each year sees more than 1,500 cases, and currently there is limited access to an intravenously-administered (IV) drug needed for the more serious cases, according to a top malaria researcher at the University of Maryland School Medicine (UMSOM).
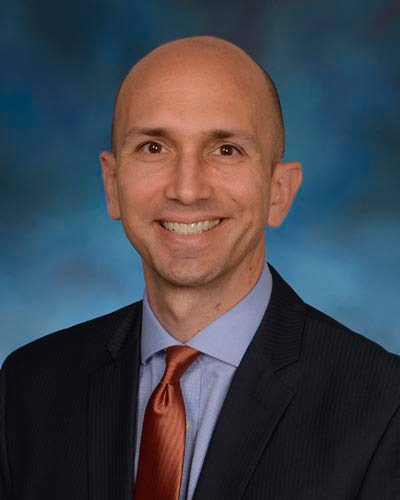

Tuesday, August 13, 2019
UM School of Medicine Researchers Begin Phase 1 Clinical Trial of Vaccine Against Mosquito-Borne Diseases
Mosquito-borne diseases including malaria, dengue and yellow fever, have a severe impact resulting in millions of deaths worldwide, hitting the world’s most vulnerable populations the hardest. Researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) have begun testing an experimental vaccine that is designed to protect against a series of these diseases.

Friday, November 02, 2018
UMSOM Global Health Expert Named to Prestigious World Health Organization Immunization Panel
Kathleen Neuzil, MD, MPH, Professor of Medicine and Pediatrics and Director of the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health (CVD) at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM), has been named to the World Health Organization’s (WHO) Strategic Advisory Group of Experts (SAGE) on Immunization.

Wednesday, June 06, 2018
UMSOM Researchers Find that Silent Carriers of Malaria are Unlikely to Develop the Disease
In regions where malaria illness is widespread, it is common to find many individuals who are infected with malaria parasites (Plasmodium falciparum), but without symptoms. New research conducted by the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) shows that treating these silent malaria cases could help stop the spread of malaria to others.

Tuesday, May 15, 2018
Tackling Malaria Transmission in Sub-Saharan Africa
Two malaria experts in the Center for Vaccine Development and Global Health at the University of Maryland School of Medicine wrote a commentary published in the June Issue of The Lancet Global Health discussing the prevalence of malaria in school-age children in sub-Saharan Africa. Miriam Laufer, MD, Associate Professor of Pediatrics and Associate Director for Malaria Research CVD, and Lauren Cohee, MD, Instructor, Pediatrics, noted that often malaria infection is more common in school-age children than younger children and adults.

Tuesday, December 06, 2016
Researchers Combine MERS and Rabies Viruses to Create Innovative 2-For-1 Vaccine
In a new study, University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM) researchers have modified a rabies virus, so that it has a protein from the MERS virus; this altered virus works as a 2-for-1 vaccine that protects mice against both Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) and rabies.