April 14, 2016
Discovery Could Eventually Lead To New and Better Treatments for Insomnia and Jet Lag
Falling asleep and waking up are key transitions in everyone’s day. Millions of people have trouble with these transitions – they find it hard to fall asleep or stay asleep at night, and hard to stay awake during the day. Despite decades of research, how these transitions work – the neurobiological mechanics of our circadian rhythm – has remained largely a mystery to brain scientists.
Now, however, scientists at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UM SOM) have identified the workings of a key pathway for these processes. The pathway that appears to play a key role in regulating the “switch” between wakefulness and sleep. This is the first study to elucidate this process in such biophysical detail.
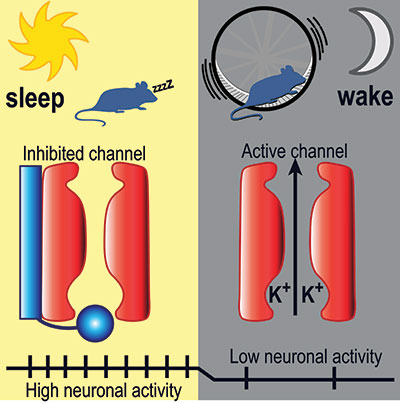
 Andrea Meredith, PhD, Associate Professor of Physiology at UM SOM, focused on a particular brain area, the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the hypothalamus. This region acts as the brain’s internal clock, determining when we feel like going to sleep, how long we sleep, and when we feel like getting up. Within the suprachiasmatic nucleus, which is known as the SCN, she focused on certain ion channels, proteins that conduct electrical current, relaying information from one neuron to another. She focused on a group of channels known as BK potassium channels, which seem to be particularly active in the SCN.
Andrea Meredith, PhD, Associate Professor of Physiology at UM SOM, focused on a particular brain area, the suprachiasmatic nucleus in the hypothalamus. This region acts as the brain’s internal clock, determining when we feel like going to sleep, how long we sleep, and when we feel like getting up. Within the suprachiasmatic nucleus, which is known as the SCN, she focused on certain ion channels, proteins that conduct electrical current, relaying information from one neuron to another. She focused on a group of channels known as BK potassium channels, which seem to be particularly active in the SCN.
In the paper, which appeared recently in Nature Communications, Dr. Meredith examined mice, whose schedule is opposite to humans – they sleep during the day and are awake at night. She found that BK channels are active during waking, which for the mice was at night; during the day the BK channels were inactive. She found that in this daytime context, the role of the BK channels is to inhibit wakefulness.
Prof. Meredith examined normal mice, along with mice that had been genetically altered so that their BK channels could not be inactivated. She then recorded activity in these channels, via electrodes placed in SCN neurons. In the brains of the genetically modified group, the animals that could not inactivate their BK channels, she found lower levels of neuronal activity, which was associated with more daytime wakefulness. This was unusual, because mice generally sleep during the day.
The new findings are surprising, for several reasons. The researchers didn’t know of any physiological process in the body that relied on BK channel inactivation as a mechanism. Scientists had known that the channel acted in this way, but didn’t know how neurons used this mechanism to regulate information coding in the brain. This is the first study to show that BK channel inactivation is critical for encoding circadian rhythm in the brain.
Previously, BK channels had been known to be important for regulating other physiological functions. They are important for activating muscles, and play a prominent role in controlling blood pressure, heart rate, and bladder function. In the brain, BK channels have been known to be involved in regulating neuronal excitability, and play a role in motor control, learning and memory. In the brain, dysfunction in BK channels is associated with tremors, seizures, addiction, and problems with learning and memory.
“We knew that BK channels were widely important throughout the body,” says Prof. Meredith. “But now we have strong evidence that they are specifically and intrinsically involved in the wake-sleep cycle. That’s really exciting.”
Also, in the past, scientists had thought that the day-night pattern of firing was largely driven by a different mechanism, the number of ion channels that exist on the surface of SCN neurons. The new paper showed that this model is too simplistic. The new study shows that the key is not the number of channels, but the fact that the channels are being activated, and more importantly, inactivated, at specific times of day.
The discovery has clinical implications. Prof. Meredith says the new understanding of the inactivation mechanism could potentially be used to develop drugs that target circadian rhythms. Such a medication could be used to treat sleep disorders, jet lag, and seasonal affective disorder, all of which involve problems with the SCN circadian clock.
“This work illustrates how our basic scientists are not only solving fascinating research questions, but are doing work that has the potential to be widely useful to doctors and patients,” said UM SOM Dean E. Albert Reece, MD, PhD, MBA, who is also Vice President of Medical Affairs, the University of Maryland and the John Z. and Akiko Bowers Distinguished Professor, University of Maryland School of Medicine. “I am excited to see how Prof. Meredith and her colleagues continue to mine this fertile area of research.”
About the University of Maryland School of Medicine
The University of Maryland School of Medicine, chartered in 1807 and as the first public medical school in the United States, continues today as an innovative leader in accelerating innovation and discovery in medicine. The School of Medicine is the founding school of the University of Maryland and is an integral part of the 12-campus University System of Maryland. Located on the University of Maryland’s Baltimore campus, the School of Medicine works closely with the University of Maryland Medical Center and Medical System to provide a research-intensive, academic and clinically based education. With 45 academic departments, centers, programs and institutes and a faculty of more than 3,000 physicians and research scientists, along with more than $400 million in extramural funding, the School is regarded as one of the leading biomedical research institutions in the U.S. with top-tier faculty and programs in cancer, brain science, surgery and transplantation, trauma and emergency medicine, vaccine development and human genomics, among other centers of excellence. The School is not only concerned with the health of the citizens of Maryland and the nation, but also has a global presence, with research and treatment facilities in more than 35 countries around the world.
medschool.umaryland.edu/
Contact
Office of Public Affairs
655 West Baltimore Street
Bressler Research Building 14-002
Baltimore, Maryland 21201-1559
Contact Media Relations
(410) 706-5260
Related stories

Thursday, January 08, 2026
Improving Sleep Isn’t Enough: Researchers Highlight Daytime Function as Key to Assessing Insomnia Treatments
About one in nine adults suffer from chronic insomnia and its residual effects like drowsiness, cognitive issues, and irritability as well as increased health risks like diabetes and heart risks if left untreated. While many treatments are available, the challenge lies in determining how well a medication or other sleep aid works in individual patients.

Thursday, November 21, 2024
UM School of Medicine Researchers Link Snoring to Behavioral Problems in Adolescents without Declines in Cognition
Adolescents who snore frequently were more likely to exhibit behavior problems such as inattention, rule-breaking, and aggression, but they do not have any decline in their cognitive abilities, according to a new study conducted by researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM). This is the largest study to date tracking snoring in children from elementary school through their mid-teen years and it provides an important update to parents struggling with what medical measures to take to help manage snoring in their children.

Friday, July 29, 2022
Children Who Lack Sleep May Experience Detrimental Impact on Brain and Cognitive Development That Persists Over Time, UM School of Medicine Study Finds
Elementary school-age children who get less than nine hours of sleep per night have significant differences in certain brain regions responsible for memory, intelligence, and well-being compared to those who get the recommended 9-12 hours of sleep per night, according to a new study led by University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researchers. Such differences correlated with greater mental health problems like depression, anxiety, and impulsive behaviors in those who lacked sleep. Inadequate sleep was also linked to cognitive difficulties with memory, problem solving and decision making. The findings were published today in the journal Lancet Child & Adolescent Health.

Wednesday, February 02, 2022
ADHD Medicine May Treat Symptoms of Genetic Movement Disorder in Children, University of Maryland School of Medicine Study Finds
Using a common attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) medication appears to help manage the symptoms of a rare and currently difficult to treat genetic movement disorder primarily found in children, according to a new study from a University of Maryland School of Medicine (UMSOM) researcher Andrea Meredith, PhD, and her collaborators.

Wednesday, January 15, 2020
Dr. Andrea Meredith’s Research is the Cover Story in The Physiologist Magazine
One night just before bed in August 2018, Andrea Meredith, PhD, was reading the New York Times Magazine on her iPad when she came across an article about a six-year-old girl in South Dakota named Kamiyah who had a mysterious disorder. Over 300 times a day, the little girl would fall or slump forward, with large portions of her body paralyzed. An episode would last anywhere from three to 20 seconds. Then, suddenly, she would pop back up and resume whatever she was doing. The article mentioned that Kamiyah had paroxysmal dyskinesia, a type of movement disorder. But the cause was unknown.

Thursday, September 28, 2017
University of Maryland School of Medicine Researchers Identify Intriguing Links Between Sleep, Cognition and Schizophrenia
More than 3.2 million Americans suffer from schizophrenia; about 100,000 people are newly diagnosed every year. The disease includes a wide range of symptoms including visual and auditory hallucinations, cognitive problems and motivational issues.

Monday, March 14, 2016
UM SOM Sleep Experts Explore the Massive Financial Toll of Insomnia
While the benefits of a good night’s sleep can be priceless, and sleeplessness imposes significant costs on the individual and society, little is known about the financial impact of treatment for sleep-related disorders.
