What is a fetal echocardiogram?
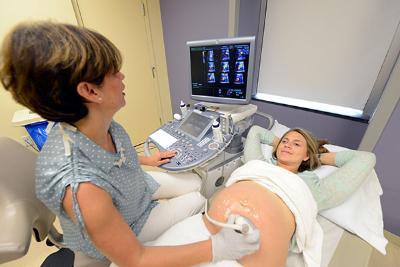
A fetal echocardiogram is performed by a fetal or pediatric cardiologist who is specially trained. The test is typically performed by placing a probe over the mother's abdomen to visualize the fetal heart. It is very similar to the ultrasound done to look at the whole baby, but focused on the baby’s heart.
During the test the transducer probe will be moved around to obtain images of different locations and structures of the fetal heart. Techniques sometimes used to obtain detailed information about the fetal heart include the following:
2-D (2-dimensional) echocardiography:
This technique is used to "see" the actual structures and motion of the heart structures. A 2-D echo view appears cone-shaped on the monitor, and the real-time motion of the heart's structures can be observed. This enables the doctor to see the various heart structures at work and evaluate them.
4-D (4- dimensional) echocardiography:
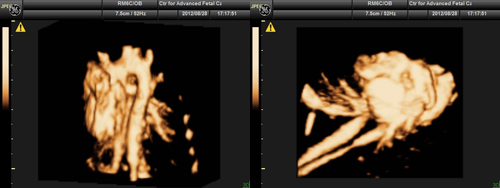 This technique is used to "see" the actual structures and motion of the heart structures as well. A 4-D echo may provide a better diagnostic approach in some of the cardiac defects. The advantages of this technique is that we can capture the images and evaluate the fetal heart even after we complete the whole study. We have an opportunity to go and review the live images again.
This technique is used to "see" the actual structures and motion of the heart structures as well. A 4-D echo may provide a better diagnostic approach in some of the cardiac defects. The advantages of this technique is that we can capture the images and evaluate the fetal heart even after we complete the whole study. We have an opportunity to go and review the live images again.
Doppler echocardiography:
This Doppler technique is used to measure and assess the flow of blood through the heart's chambers and valves. The amount of blood pumped out with each beat is an indication of the heart's functioning. Also, Doppler can detect abnormal blood flow within the heart, which can indicate such problems as an opening between chambers of the heart, a problem with one or more of the heart's four valves, or a problem with the heart's walls.
Color Doppler:
Color Doppler is an enhanced form of Doppler echocardiography. With color Doppler, different colors are used to designate the direction of blood flow. This simplifies the interpretation of the Doppler images.
What is the other procedures you may need if there is a diagnosed heart defect in your baby?
Additional ultrasounds or echocardiography. Tests done to confirm the diagnosis, follow fetal growth, and monitor fetal well-being.
.jpg) Chorionic Villus Sampling or Amniocentesis:
Chorionic Villus Sampling or Amniocentesis:
Chorionic villous sampling (CVS) is a prenatal test. It’s used to diagnose certain birth defects and genetic abnormalities in your baby. Whenever we find a cardiac defect in the baby, CVS is one of the prenatal testing options available to you. During this procedure your health care provider takes a small piece of tissue from the placenta. The sample is used to check your baby’s genetic material, in the form of chromosomes, extra genetic material (duplications) or missing genetic material (deletions). This test could be performed between 11 and 14 weeks of pregnancy. 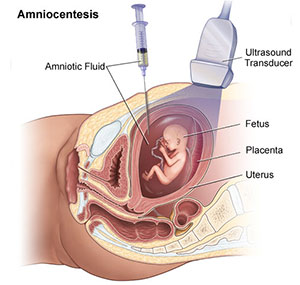 One advantage of this test is that you can find out some genetic problems your baby might have from the beginning of the pregnancy. There is a small miscarriage risk associated with this test and your genetic counselor will explain to you the risks during the counseling session.
One advantage of this test is that you can find out some genetic problems your baby might have from the beginning of the pregnancy. There is a small miscarriage risk associated with this test and your genetic counselor will explain to you the risks during the counseling session.
Amniocentesis is also a prenatal test. It’s used to diagnose certain birth defects and genetic abnormalities in your baby like a CVS. This time instead of placental tissue we obtain a small amount of amniotic fluid for testing. This test could be performed anytime after 16 weeks in pregnancy. There is a small miscarriage risk associated with this test also and your genetic counselor will explain to you the details and risks of the test during the counseling session.
