CONTACT:

Marcelo Sztein, MD
Laboratory Director
msztein@medicine.umaryland.edu
410-706-2345
Regina Harley, MS
Laboratory Supervisor
rharley@som.umaryland.edu
410-706-0095
LOCATION:
Room 456, Health Sciences Facility I
685 West Baltimore Street
Baltimore, MD 21201
HOURS:
Monday through Friday
7:00am - 5:00pm
PHONE:
Office: 410-706-0095
Fax: 410-706-6205
Email: cvdflowcore@medicine.umaryland.edu
LABORATORY POLICIES:
Experiments should preferably be scheduled one to two weeks in advance.
All sample analysis and cell sorting is done by Core Laboratory personnel.
The “Rules and Regulations” form (Revision March 10, 2015) is available at the CVD Flow Cytometry Core Laboratory
MISSION:
To ensure that University of Maryland investigators have access to flow cytometry and mass cytometry services for their research. A facility with dedicated operators ensures well-performing instruments and optimal results with a minimal outlay of expenses. Established in 1991, this facility has state-of-the art equipment and a highly-trained and experienced staff.
SERVICES:
Multichromatic flow cytometry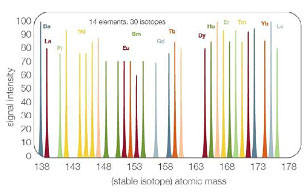
Including markers for:
- Lineage
- Maturation
- Activation
- Homing
- Intracellular cytokines
- Cell sorting (up to 6-way)
based on GFP and/or multichromatic staining - Mass Cytometry (>60 parameters)
- Serum/supernatant cytokine levels using bead kits (e.g. BD Pharmingen CBA kit)
- Cell cycle analysis (PI, DAPI)
- Cell proliferation (CFSE, PCNA, BrdU and Ki67)
- Apoptosis (Annexin V vs. PI; TUNEL; subG0/G1 peak analysis)
- Green fluorescence protein (GFP) (eukaryotic and prokaryotic)
- Advice with experimental design and data analysis
INSTRUMENATION:
BD LSR II Flow Cytometer:

- 4 lasers: 407, 488, 552, and 641 nm
- 16 parameters (14 colors plus forward and side scatter)
Beckman Coulter MoFlo Astrios Cell Sorter

- 4 lasers: 355, 407, 488, and 641 nm
- 21 parameters (19 colors plus forward and side scatter)
- Up to 6-way high speed sorting
- CyCLONE single cell sorting
Fluidigm CyTOF Mass Cytometer

- >35 parameters based on mass spectrometry detection of metal isotope- labeled antibody staining
- No need for single color controls or fluorescence compensation
Fluidigm Helios Mass Cytometer

- >60 parameters based on mass spectrometry detection of metal isotope- labeled antibody staining
- No need for single color controls or fluorescence compensation
Principles of Flow Cytometry
Fluidics
- Cells in a single-cell suspension
- Flow in a single file through
Optics
- An illuminated volume where they
- Scatter light and emit fluorescence
- That is filtered, collected and
Electronics
- Converted to digital values
- That are stored on a computer
- And put through software for analysis
Revised from Dr. Robert Murphy, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA
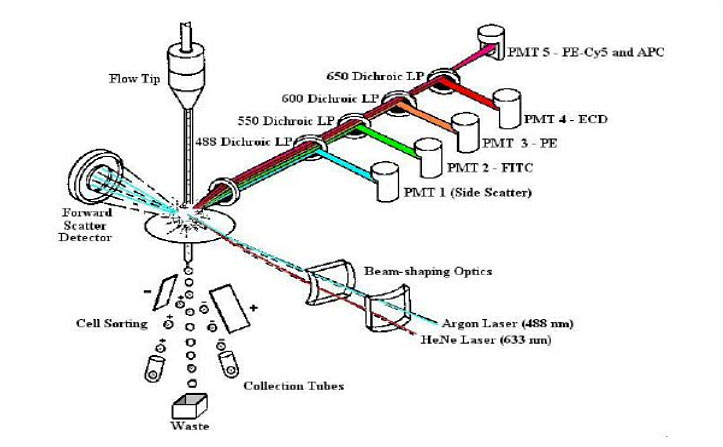
Principles of Mass Cytrometry
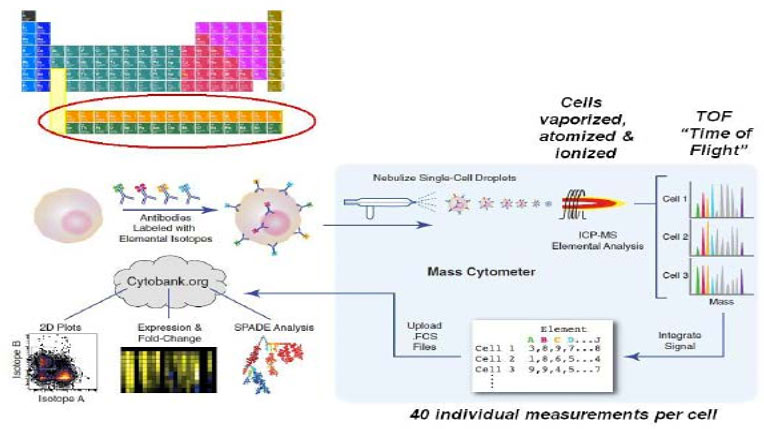
Bendall & Simonds et al., Science 332, 687 (2011) www.cytobank.org/nolanlab