CONTACT:

Olga G. Goloubeva, PhD, MSc
Director
Biostatistics Shared Services
ogoloubeva@som.umaryland.edu
Appointments and Information
Susan Holt
Office Manager
sholt@som.umaryland.edu
LOCATION:
Department of Epidemiology and Public Health
Division of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics
660 W. Redwood Street, HH109
Baltimore, MD 21201
HOURS:
Monday through Friday
7:00am - 5:00pm
PHONE:
410-706-8505
Fax: 410-706-8548
Our most important resource is our team of enthusiastic and competent biostatisticians, bioinformaticians and administrative staff. We have expertise in many fields of ‘traditional’ biostatistics, including study/trial design and multivariable statistical modeling, but also in bioinformatics, high-dimensionality data sets, machine learning, supervised and unsupervised data analysis, mathematical modeling, simulations and much more! We perform statistical programming as needed. Major statistical software available includes SAS, R, Splus, SPSS, Stata, StatXact and East. We also develop customized computer programs for complex statistical problems.
Picture (left-right back) Larry Magder, Clayton Brown, Søren Bentzen, William Wooten, Shuo Chen, Lei Wang (left-right front) Helen Powell, Yuji Zhang, Olga Goloubeva, Yuanyuan Liang, Min Zhan, Susan Holt. Not pictured: Hegang Chen, Owen White
MISSION:
Quantitative biomedical research is a team sport. The biostatistician brings a strong foundation in statistics, mathematics and computational methods, augmented by knowledge of the field of application and familiarity with biomedical concepts and terminology.
Our most important resource is our team of enthusiastic and competent biostatisticians, bioinformaticians and administrative staff. We have expertise in many fields of ‘traditional’ biostatistics, including study/trial design and multivariable statistical modeling, but also in bioinformatics, high-dimensionality data sets, machine learning, supervised and unsupervised data analysis, mathematical modeling, simulations and much more! We perform statistical programming as needed. Major statistical software available includes SAS, R, Splus, SPSS, Stata, StatXact and East. We also develop customized computer programs for complex statistical problems.
SERVICES:
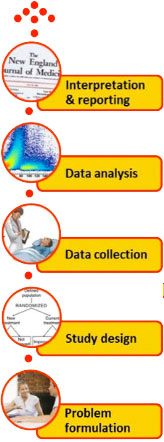 We collaborate on all aspects of design, analysis, interpretation, and reporting of quantitative biomedical research.
We collaborate on all aspects of design, analysis, interpretation, and reporting of quantitative biomedical research.
How Can We Help?
Biostatisticians are involved in the whole chain of quantitative biomedical research: from early formulation of research aims, to the final interpretation and reporting of study outcomes.
We like to be involved all the way. Decisions made at the study design stage will often dictate what you will be able to do when it comes to data analysis — and may ultimately affect what you can conclude from your study.
A Few Practical Notes:
- The biostatistics service runs by appointment only; however, we do offer free office hours for quick questions (10-20 minutes on Tuesdays at Noon.
- We will try to link you up with a biostatistician who has domain expertise and/or relevant methodology expertise AND available time.
- It takes time to set up an appointment, to provide advice and to act on the advice — last-minute consultations may not produce optimal service and are discouraged.
- We do not provide individual tutoring as a substitute for proper biostatistics education (e.g., as part of a degree program).
- For input to a grant proposal and for significant input to a research project or a data analysis, the biostatistician should be included as a co-investigator.
Research:
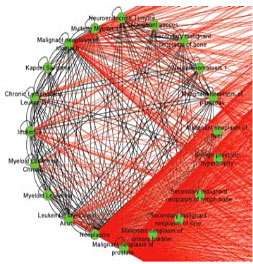 Example 1: Association network related to “Malignant neoplasm of prostate” and “leukaemia” using the Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) based topic modelling approach. Cancer Informatics 2014; 13: 45-51.
Example 1: Association network related to “Malignant neoplasm of prostate” and “leukaemia” using the Latent Dirichlet allocation (LDA) based topic modelling approach. Cancer Informatics 2014; 13: 45-51.
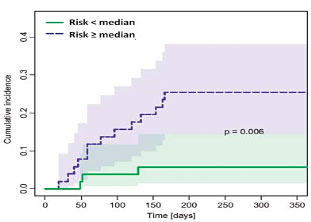 Example 2: Cumulative incidence of radiation pneumonitis for patients in an independent validation cohort grouped according to predicted risk. Shaded areas: 95% confidence intervals. Acta Oncol. 2014;53(5):605-12.
Example 2: Cumulative incidence of radiation pneumonitis for patients in an independent validation cohort grouped according to predicted risk. Shaded areas: 95% confidence intervals. Acta Oncol. 2014;53(5):605-12.
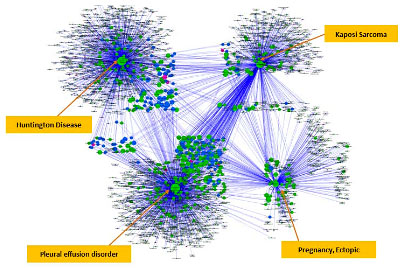
Example 3: Overview of Huntington disease-specific association network. In total, there are 3316 associations among 2499 biological entities (1253 diseases, 1131 chemical drugs, and 115 genes). Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine 2013, 72-75.