Academic Title:
Professor
Primary Appointment:
Pharmacology & Physiology
Secondary Appointment(s):
Surgery
Administrative Title:
Associate Director of Research; Acting Director of CVID
Location:
BioPark1-R211 800 W Baltimore Street, Baltimore, MD 21201
Phone (Primary):
410-706-8040
Fax:
410-706-8121
Education and Training
I received my PhD in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and did my postdoctoral training at the University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, Indiana. I worked at the Lerner Research Institute of the Cleveland Clinic Foundation and the Holland Laboratory of the American Red Cross before joining the faculty of the University of Maryland, School of Medicine. My research program has been continuously funded and supported by the National Institute of Health. I also get research support from the Department of Defense, Arthritis Foundation, and the American Heart Association.
Research/Clinical Keywords
Cardiovascular diseases, Autoimmunity, inflammation, stem cells, macrophages, integrin, cell adhesion
Highlighted Publications
Zhang, L., Jhingan, A., and Castellino, F.J. (1992) Role of individual g-carboxyglutamic acid residues of activated human protein C in defining its in vitro anticoagulant activity. Blood, 80: 942-952.
Cao, C., Lawrence, D.A., Strickland, D., and Zhang, L. (2005) A specific role of integrin mac-1 in accelerated macrophage efflux to the lymphatics. Blood, 106: 3234-3241, 2005. Also see commentary “Mac-1 mediates migration to lymph nodes” by Joseph P. Mizgerd (Blood 106:2927-2928).
Cao, C., Lawrence, D.A., Li, Y., Von Arnim, C.A., Herz, J., Su, EJ, Makarova, A, Hyman, B.T., D.A., Strickland, D., and Zhang, L. (2006) Endocytic receptor LRP together with tPA and PAI-1 coordinates Mac-1-dependent macrophage migration. The EMBO Journal, 25:1860-1870.
Ehirchiou, D., Xiong, Y., Xu, G., Chen, W., Shi, Y., and Zhang, L. (2007) CD11b Facilitates the Development of Peripheral Tolerance by Suppressing Th17 Differentiation. Journal Experimental Medicine 204:1519-24.
Malinin, N., Zhang, L., Choi, J., Ciocea, A., Razorenova, O., Ma, Y., Podrez, E.A., Tosi, M., Lennon, D.P., Caplan, A.I., Shurin, S.B., Plow, E.F., and Byzova, T.V. (2009) A point mutation in kindlin-3 ablates activation of three integrin subfamilies in humans. Nature Medicine 15:313-8. PMCID: PMC2857384
Cao, C., Gao, Y., Li, Y., Antalis, T., Castellino, F.J., and Zhang, L. (2010) The Efficacy of Activated Protein C in Murine Endotoxemia Is Dependent on Integrin CD11b. Journal of Clinical Investigation 120:1971-1980, Highlighted on Faculty of 1000 Biology, July 2010. PMCID: PMC2877939
Yakovlev, S., Belkin, A.M., Chen, L., Cao, C., Zhang, L., Strickland, D.K., Medved, L. (2016) Anti-VLDL receptor monoclonal antibodies inhibit fibrin-VLDL receptor interaction and reduce fibrin-dependent leukocyte transmigration. Thromb Haemost. Nov 30;116(6):1122-1130. Epub 2016 Sep 1. PMCID: PMC5294920
Skerry, C., Scanlon, K., Ardanuy, J., Roberts, D., Zhang, L., Rosen, H., Carbonetti, N.H. (2017) Therapeutic treatment with sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 ligands reduces pertussis inflammatory pathology by a pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Infect Dis. 215:278-286. PMCID: PMC5853922
Stevanin, M., Busso, N., Chobaz, V., Pigni, M., Ghassem-Zadeh, S., Zhang, L., Acha-Orbea, H., Ehirchiou, D. (2017) CD11b regulates via IL-6 the Treg/Th17 balance in murine arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol, 47:637-645. PMID: 28191643
Su, E.J., Cao, C., Fredriksson, L., Nilsson, I., Stefanitsch, C., Stevenson, T.K., Zhao, J., Ragsdale, M., Sun, Y., Yepes, M., Kuan, C.Y., Eriksson, U., Strickland, D.K., Lawrence, D.A., and Zhang, L. (2017) Microglial mediated PDGF-CC activation increases cerebrovascular permeability during ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol 134:585–604. PMCID: PMC5587628
Zhang, L. (2018) Contribution of resident and recruited macrophages in vascular physiology and pathology. Current Opinion in Hematology, 25:196-203. PMID: 29438258
Additional Publication Citations
Zhang, L. and Castellino, F.J. (1989) Generation of an antibody with a designed specificity difference for protein C and activated protein C. Journal of Protein Chemistry, 8:471-480.
Zhang, L. and Castellino, F.J. (1990) A g-carboxyglutamic acid (g variant g6D,g7D) of human activated protein C displays greatly reduced activity as an anticoagulant. Biochemistry, 29:10828-10834.
Zhang, L. and Castellino, F.J. (1991) The role of the hexapeptide disulfide loop present in g-carboxyglutamic acid domain of human activated protein C in its in vitro anticoagulant properties. Biochemistry, 30: 6696-6704.
Zhang, L., Jhingan, A., and Castellino, F.J. (1992) Role of individual g-carboxyglutamic acid residues of activated human protein C in defining its in vitro anticoagulant activity. Blood, 80: 942-952.
Zhang, L. and Castellino, F.J. (1992) Influence of specific g-carboxyglutamic acid residues on the integrity of the calcium-dependent conformation of human protein C. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267: 26078-26084.
Zhang, L. and Castellino, F.J. (1993) The contributions of individual g-carboxyglutamic acid residues in the calcium-dependent binding of recombinant human protein C to acidic phospholipid vesicles. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268: 12040-12045.
Yu. S., Zhang, L., Jhingan, A., Christiansen, W.T. and Castellino, F.J. (1994) Construction, expression, and properties of a recombinant chimeric human protein C with replacement of its growth factor-like domains by those of human coagulation factor IX. Biochemistry, 33: 823-831.
Zhang, L., and Castellino, F.J. (1994) The binding energy of human coagulation protein C to acidic phospholipid vesicles contains a major contribution from leucine 5 in the g-carboxyglutamic acid domain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269: 3590-3595.
Jhingan, A., Zhang, L., Christiansen, W.T. and Castellino, F.J. (1994) The activities of recombinant g-carboxyglutamic acid-deficient mutants of activated human protein C toward human coagulation factor Va and factor VIII in purified systems and in plasma. Biochemistry, 33: 1869-1875.
Zhang, L., Muchowski, P.J., Chang, E.R., Soule, H.R., Plow, E.F. and Moyle, M. (1994) Functional interaction between the integrin antagonist NIF and the I domain of CD11b/CD18. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269: 26419-26423.
Zhang, L., and Plow, E.F. (1996) Overlapping, but not identical, sites are involved in the recognition of C3bi, neutrophil inhibitory factor, and adhesive ligands by the CD11b/CD18 integrin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271: 18211-18216.
Zhang, L., and Plow, E.F. (1996) A discrete site modulates activation of I domains: application to integrin aMb2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271: 29953-29957.
Zhang, L., and Plow, E.F. (1997) Identification and reconstruction of the binding site within aMb2 for a specific and high affinity ligand, NIF. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272: 17558-17564.
Plow, E.F. and Zhang, L. (1997) A MAC-1 attack: integrin functions directly challenged in knock-out mice. Journal of Clinical Investigation 99:1145-1146.
Zaffran, Y., Zhang, L., and Ellner J.J. (1998) Role of CR4 in mycobacterium tuberculosis human macrophages binding and signal transduction in the absence of serum. Infection and Immunity, 66(9): 4541-4.
Forsyth, C.B., Plow, E.F., and Zhang, L. (1998) Interaction of the fungal pathogen Candida Albicans with integrin CD11b/CD18: Recognition by the I domain is modulated by the lectin-like domain and the CD18 subunit.Journal of Immunology, 161: 6198-6205.
Ugarova, T.P., Solovjov, D.A., Zhang, L., Loukinov, D.I., Yee, V.C., Medved, L.V., and Plow, E.F. (1998)Identification of a novel recognition sequence for integrin aMb2 within the g-chain of fibrinogen. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273: 22519-22527.
Cierniewski, C.S., Byzowa, T., Papierak, M., Haas, T.A., Niewiarowska, J., Zhang, L., Cieslak, M., and Plow, E.F. (1999) Peptides that mimic natural contact points of fibrinogen for aIIbb3 bind simultaneously to distinct subsites on the receptor and induce differential conformational and microenvironmental changes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274: 16923-16932,
Zhang, L. (1999) The aMb2 integrin and its role in neutrophil function. Cell Research 9:171-178.
Zhang, L., and Plow, E.F. (1999) Amino acid sequences within the alpha subunit of integrin aMb2 (Mac-1) critical for specific recognition of C3bi. Biochemistry, 38: 8064-8071.
Simon, D.I., Chen, Z., Xu, H., Li, C.Q., Dong, J., McIntire, L.V., Ballantyne, C.M., Zhang, L., Furman, M.I., Berndt, M.C., and Lopez, J.A. (2000) Platelet glycoprotein ibalpha is a counterreceptor for the leukocyte integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18). Journal of Experimental Medicine 192:193-204.
Simon, D.I., Wei, Y., Zhang, L., Rao, N.K., Xu, H., Chen, Z., Liu, Q., Rosenberg, S., and Chapman, H.A. (2000)Identification of a urokinase receptor-integrin interaction site: promiscuous regulator of integrin function. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275: 10228-10234.
Plow, E.F., Haas, T.A., Zhang, L., Loftus, J. and Smith, J.W. (2000) Ligand binding to integrins. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275:21785-21788.
Yakubenko, V.P., Solovjov, D.A., Zhang, L., Yee, V.C., Plow, E.F., and Ugarova, T.P. (2001) Identification of the binding site for fibrinogen recogntion peptide g383-395 within the aMI-domain of integrin aMb2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276: 13995-14003.
Xiong, Y. M., and Zhang, L. (2001) Structure-function of the putative I-domain within the integrin b2 subunit. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276: 19340-19349.
Xiong, Y. M., Haas, T.A., and Zhang, L. (2002) Identification of Functional Segments within the b2I-domain of Integrin alphaM beta2. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277: 46639-46644.
Cierniewska-Cieslak, A., Cierniewski, C.S., Blecka, K., Papierak, M., Michalec, L., Zhang,L., Haas, T.A., and Plow, E.F. (2002) Identification and characterization of two cation binding sites in the integrin beta 3 subunit. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277: 11126-11134.
Castellino, F.J., Ploplis, V.A. and Zhang, L. (2002) g-glutamate and b-Hydroxyaspartate in Proteins. Posttranslational Modifications of Proteins: Tools for Functional Proteomics. Edited by C. Kannicht, Chapter 17, page 259-268.
Li, Y. and Zhang, L. (2003) The fourth blade within the beta-propeller is involved specifically in C3bi recognition by integrin alphaM beta2. Journal of Biological Chemistry 278:34395-34402.
Xiong, Y. M., Chen, J., and Zhang, L. (2003) Modulation of CD11b/CD18 adhesive activity by its extracellular membrane-proximal regions. Journal of Immunology 171:1042-1050.
Li, Y., D.A. Lawrence, D.A., and Zhang, L. (2003) Sequences within Domain II of the Urokinase Receptor Critical for Differential Ligand Recognition. Journal of Biological Chemistry 278: 29925-29932.
Ehirchiou, D., Xiong, Y.M., Li, Y., Brew, S., and Zhang. L. (2005) Dual function for a unique site within the b2I-domain of integrin alphaMbeta2. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280:8324-8331.
Cao, C., Lawrence, D.A., Strickland, D., and Zhang, L. (2005) A specific role of integrin mac-1 in accelerated macrophage efflux to the lymphatics. Blood, 106: 3234-3241, 2005. Also see commentary “Mac-1 mediates migration to lymph nodes” by Joseph P. Mizgerd (Blood 106:2927-2928).
Yakovlev, S., Zhang, L., Ugarova, T., and Medved, L. (2005) Interaction of Fibrin(ogen) with Leukocyte Receptor alpha(M)beta(2) (Mac-1): Further Characterization and Identification of a Novel Binding Region within the Central Domain of the Fibrinogen gamma-Module. Biochemistry 44:617-26.
Miura, Y., Miura, M., Gronthos, S., Allen, M.R., Cao, C., Uveges, T.E., Bi, Y., Shi, S., and Zhang, L. (2005) Integrin beta2 is a novel surface marker for bone marrow stromal stem cells and plays an important role in osteogenic differentiation in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 102:14022-14027. see Report on SOM news vol7 number 4, page 2.
Cao, C., Lawrence, D.A., Li, Y., Von Arnim, C.A., Herz, J., Su, EJ, Makarova, A, Hyman, B.T., D.A., Strickland, D., and Zhang, L. (2006) Endocytic receptor LRP together with tPA and PAI-1 coordinates Mac-1-dependent macrophage migration. The EMBO Journal, 25:1860-1870.
Xiong, Y., Cao, C., Makarova, A., Hyman, B., and Zhang, L. (2006) Mac-1 promotes FcgRIIA-dependent cell spreading and migration on immune complexes. Biochemistry 45:8721-31.
Miura, Y., Gao, Z., Miura, M., Seo, B.M., Sonoyama, W., Chen, W., Gronthos, S., Zhang, L., and Shi, S. (2006)Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Organized Bone Marrow Elements: An Alternative Hematopoietic Progenitor Resource. Stem Cells 24:2428-2436.
Tang, P., Cao, C., Xu, M., and Zhang, L. (2007) Regulation of integrin activation by cytoskeletal protein Radixin. FEBS Letters 581:1103-1108.
Ehirchiou, D., Xiong, Y., Xu, G., Chen, W., Shi, Y., and Zhang, L. (2007) CD11b Facilitates the Development of Peripheral Tolerance by Suppressing Th17 Differentiation. Journal Experimental Medicine 204:1519-24.
see Commentary by Bashyam "CD11b tunes tolerance" J Exp Med 204:1504.
see Commentary by Budde "The Behavior of Th17 Cells Is Intolerable" CELL 130:7, 2007
see News and Commentary by Veldhoen "Oral Tolerance: Passing CD11b on the Way to Tolerance"Immunology and Cell Biology85:397-398.
Bi, Y., Ehirchiou, D., Kilts, T.M., Inkson, C.A., Embree, M.C., Sonoyama, W., Li, L., Leet, A.I., Seo, B., Zhang, L., Shi, S., and Young, M.F. (2007) Identification of tendon stem/progenitor cells and the role of the extracellular matrix in their niche. Nature Medicine. 13:1219-1227.
Choi, E.Y., Orlova, V.V., Fagerholm, S.C., Nurmi, S.M., Zhang, L., Ballantyne, C.M., Gahmberg, C.G., Chavakis, T. (2008) Regulation of LFA-1-dependent inflammatory cell recruitment by Cbl-b and 14-3-3 proteins. Blood111:3607-14. PMCID: PMC2275024
Li, Y., Cao, C., Jia, W., Yu, L., Mo, M., Wang, Q., Huang, Y., Lim, J., Ishihara, M., Wells, L., Azadi, P., Robinson, H., He, Y., Zhang, L. and Mariuzza, R.A. (2009) Structure of the F-spondin domain of mindin, an integrin ligand and pattern recognition molecule. EMBO J. 28:286-97. PMCID: PMC2637340
Malinin, N., Zhang, L., Choi, J., Ciocea, A., Razorenova, O., Ma, Y., Podrez, E.A., Tosi, M., Lennon, D.P., Caplan, A.I., Shurin, S.B., Plow, E.F., and Byzova, T.V. (2009) A point mutation in kindlin-3 ablates activation of three integrin subfamilies in humans. Nature Medicine 15:313-8. PMCID: PMC2857384
Danese, S., Vetrano, S., Zhang, L., Poplis, V.A., Castellino, F.J. (2010) The protein C pathway in tissue inflammation and injury: pathogenic role and therapeutic implications. Blood 115:1121-30. PMCID: PMC2920225
Bi, Y., Gao, Y., Ehirchiou, D., Cao, C., Kikuiri, T., Le, A., Shi, S., and Zhang, L. (2010) Bisphosphonates Cause Osteonecrosis of the Jaw-like Disease in Mice. American Journal of Pathology, 177:280-90, 2010. PMCID: PMC2893671
Cao, C., Gao, Y., Li, Y., Antalis, T., Castellino, F.J., and Zhang, L. (2010) The Efficacy of Activated Protein C in Murine Endotoxemia Is Dependent on Integrin CD11b. Journal of Clinical Investigation 120:1971-1980, Highlighted on Faculty of 1000 Biology, July 2010. PMCID: PMC2877939
Ranganathan, S., Cao, C., Catania, J., Migliorini, M., Zhang, L.#, and Strickland, D. K#. Molecular Basis for the Interaction of Low Density Lipoprotein Receptor-related Protein 1 (LRP1) with Integrin αMβ2: IDENTIFICATION OF BINDING SITES WITHIN αMβ2 FOR LRP1. J Biol Chem 286:30535-30541, 2011. #, co-corresponding authors. PMCID: PMC3162413
Wolf, D., Hohmann, J.D., Wiedemann, A., Bledzka, K., Blankenbach, H., Marchini, T., Gutte, K., Zeschky, K., Bassler, N., Hoppe, N., Rodriguez, A.O., Herr, N., Hilgendorf, I., Stachon, P., Willecke, F., Duerschmied, D., von Zur Muhlen, C., Soloviev, D.A., Zhang, L., Bode, C., Plow, E.F., Libby, P., Peter, K., Zirlik, A. (2011) Binding of CD40L to Mac-1's I-Domain Involves the EQLKKSKTL Motif and Mediates Leukocyte Recruitment and Atherosclerosis--But Does Not Affect Immunity and Thrombosis in Mice. Circ Res. 109:1269-79. PMCID: PMC3291815
Yakovlev, S., Gao, Y., Cao, C., Chen, L., Strickland, D. K., Zhang, L. #, and Medved, L#. Interaction of fibrin with VE-cadherin and anti-inflammatory effect of fibrin-derived fragments. J.Thromb.Haemost. 9:1847-1855, 2011. #, co-corresponding authors. PMCID: PMC3166367
Yakovlev, S., Mikhailenko, I., Cao, C., Zhang, L., Strickland, D.K., Medved, L. (2012) Identification of VLDLR as a novel endothelial cell receptor for fibrin that modulates fibrin-dependent transendothelial migration of leukocytes. Blood 119:637-44. PMCID: PMC3257021
Gabre, J, Chabasse, C, Cao, C, Mukhopadhyay, S, Siefert, S, Bi, Y, Netzel-Arnett, S, Sarkar, R, and Zhang, L. (2014) Activated Protein C Accelerates Venous Thrombus Resolution through Heme Oxygenase-1 Induction. J.Thromb.Haemost.12:93-102. PMCID: PMC3891561
Cao, C, Zhao, J, Doughty, EK, Migliorini, M, Strickland, DK, Kann, MG, Zhang, L. (2015) Mac-1 regulates IL-13 activity in macrophages by directly interacting with IL-13Rα1. J Biol Chem. PMID: 26160172
Zheng C, Yang Q, Xu C, Shou P, Cao J, Jiang M, Chen Q, Cao G, Han Y, Li F, Cao W, Zhang L, Zhang L, Shi Y, Wang Y. CD11b regulates obesity-induced insulin resistance via limiting alternative activation and proliferation of adipose tissue macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 112:E7239-48, 2015. PMCID: PMC4702980
Yakovlev S, Cao C, Galisteo, R, Zhang L, Strickland DK, Medved L. Fibrin-VLDL receptor-dependent pathway promotes leukocyte transmigration by inhibiting Src kinase Fyn and is a target for fibrin β15-42 peptide. Thromb Haemost. 119:1816-1826, 2019.
Research Interests
My laboratory studies specific leukocyte populations in health and disease, with a major focus on the function of integrin CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1, αMβ2, or CR3). We investigate the role of innate and adaptive immunity, blood coagulation, and stem cells in disease development, tissue repair and regeneration. Projects range from structure-function analysis, leukocyte trafficking, signal transduction, to mouse models of inflammatory diseases, including atherosclerosis/restenosis, stroke, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and inflammatory bowel disease. We conduct protein modeling and site-directed mutagenesis to identify protein-protein interactions, generate knockout and knockin mice by CRISPR to study their functions, and design peptide inhibitors and sequence-specific antibodies to block their contribution to disease development.
We have been studying the molecular mechanisms that allow leukocytes to migrate within a fibrin-rich inflammatory environment and found that efficient macrophage migration requires coordination of integrin Mac-1, endocytic receptor LRP1, the serine protease tPA and its inhibitor PAI-1 (Fig. 1).
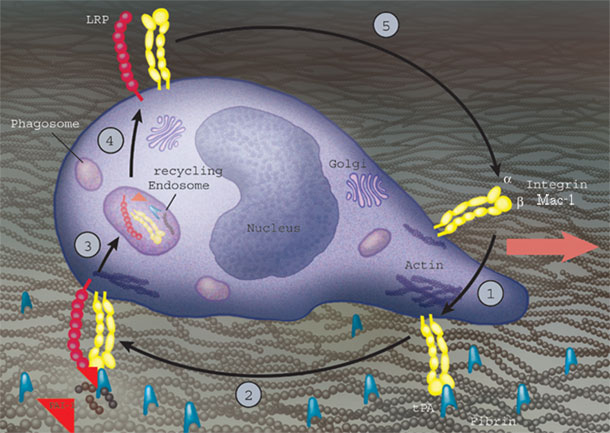
Fig. 1. Macrophage migrate by attaching to tPA/fibrin via Mac-1 (step 1), followed by PAI-1 binding to tPA (step 2) and endocytosis of the complex by LRP1 (step 3). Cao, et al. EMBO J. 2006
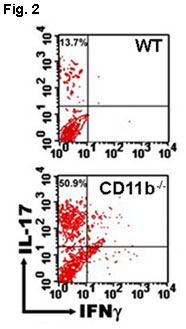 We are also investigating the nature of the CD11b/CD18 ligands that confer macrophages with proinflammatory or anti-inflammatory activities, based on our discovery that genetic inactivation of CD11b leads to the generation of T helper 17 (Th17) cells, a major subset of pathological T cells in many inflammatory diseases (Fig. 2), and the failure to develop immune tolerance in mice (J. Exp Med, 2007).
We are also investigating the nature of the CD11b/CD18 ligands that confer macrophages with proinflammatory or anti-inflammatory activities, based on our discovery that genetic inactivation of CD11b leads to the generation of T helper 17 (Th17) cells, a major subset of pathological T cells in many inflammatory diseases (Fig. 2), and the failure to develop immune tolerance in mice (J. Exp Med, 2007).
Fig. 2 (right): CD11b suppresses Th17 differentation. Ehirchiou, et al. J Exp Med 2007
In addition, we reported that CD11b enhances the anti-inflammatory function of macrophages via the activated Protein C (APC), protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1), and the sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor (Fig. 3; J. Clin Inv 2010).
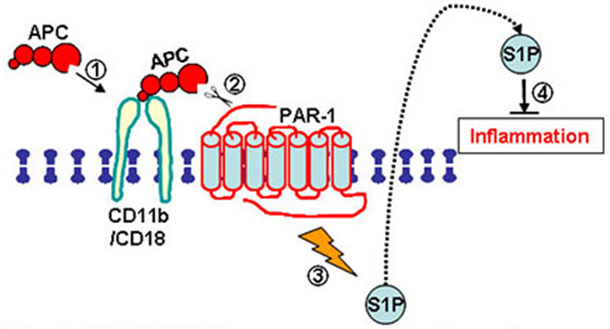
Fig. 3. CD11b enhances the anti-inflammatory function of macrophages by facilitating the activation of PAR-1 and the production of S1P, which suppresses inflammation via its receptor S1P1. Cao, et al. J Clin Inv., 2010
Our novel observations are validated independently by a number of laboratories and further supported by subsequent genome wide association studies (GWAS) in human patients where a loss-of-function variant of CD11b (R77H) is genetically linked to increased risks of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
Macrophages are derived from different embryonic origins (Fig. 4) with distinct functions in health and diseases.
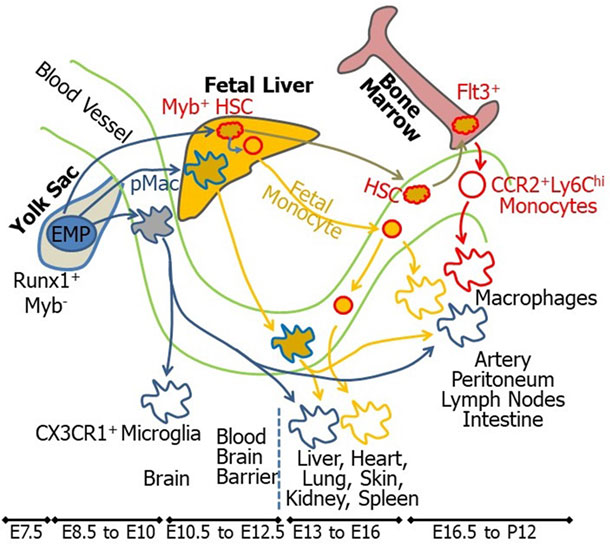
Fig. 4. Different origins of inflammatory and resident macrophages. Zhang, Curr Opin Hematol, 2018
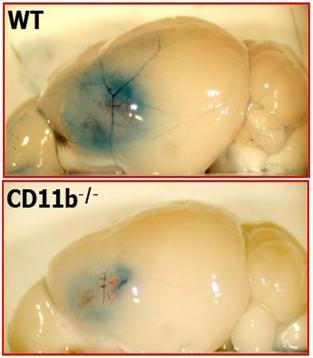
We are currently investigating the roles of inflammatory vs. resident macrophages in the pathogenesis of various cardiovascular and inflammatory diseases, including atherosclerosis and multiple sclerosis. For example, we reported recently that CD11b on microglia (resident macrophages in the brain) is key to the opening of the blood brain barrier following ischemic stroke (Fig. 5).
Finally, we are studying how stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells (Fig. 6), respond to drug treatments, e.g. bisphosphonates and antiresorptive drugs, in tissue repair and regeneration (Fig. 7).
Fig. 5. CD11b deficiency reduces the opening of the blood brain barrier. Su, et al, Acta Neuropathol, 2017
The information generated from these studies can assist us in the design of therapeutic reagents that will selectively target the deleterious effects of leukocyte engagement, such as their contributions to pathogenesis of atherosclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and other autoimmune diseases, while keeping its host defense functions intact.
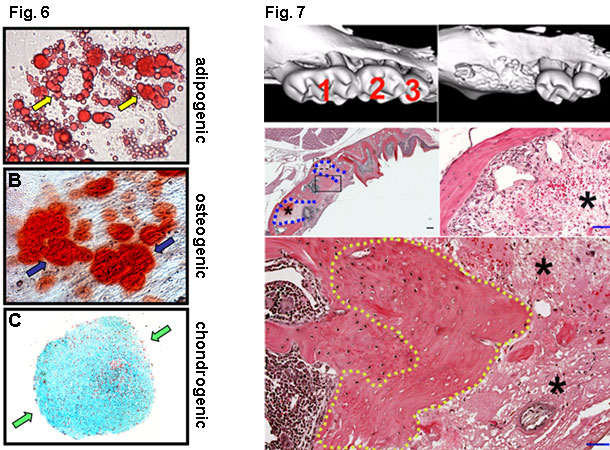
Fig 6: Differentation of mesenchymal stem cells. Miura, et al. PNAS, 2005
Fig 7: Tooth extraction leads to blood coagulation and fibrin deposition, followed by bone regeneration and remodeling. Bi, et al. AJP, 2010
Our major research projects include:
- Structure-function relationship of the CD18 integrins using the CRISPR technology to identify specific ligands that either promote or suppress inflammation in vitro and their role in health and disease in vivo.
- Resident vs. Inflammatory macrophages in inflammation and its resolution.
- Aortic resident macrophages and their role in atherosclerosis.
- Microglia in the progression and remission of progressive multiple sclerosis.
- Mesenchymal stem cells of different embryonic origins in bone repair and regeneration.
Awards and Affiliations
Professional Affiliations
- Center for Vascular and Inflammatory Diseases, University of Maryland School of Medicine
- Graduate Program in Life Science, University of Maryland Baltimore
- Program in Oncology, University of Maryland School of Medicine
- Molecular Microbiology and Immunology, University of Maryland School of Medicine
- Center for Stem Cell Biology & Regenerative Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine
Professional Activities:
- Editorial Board member, Current Drug Targets, Bentham Science Publishers
- Ad-hoc, Special Emphasis Panel ZRG1 VH-C (02) M Vascular and Hematology Study Section, NIH
- Member, K99 Application ZGM1 TWD-A KR Study Section, NIH
- Member, Fellowship Vascular Wall Biology Basic 2 Study Group, American Heart Association
- Co-Chair, Special Emphasis Panel on Emerging Technologies in Neuroscience ZRG1 ETTN-D (02), NIH
- Ad-hoc, Cellular and Molecular Biology of Glia (CMBG) Section Study Section, NIH
- Ad-hoc, ZRG1 MDCN-Q 04 M, Molecular, Cellular, and Biophysical Neuroscience, NIH
- Ad hoc member, Haemostasis and Thrombosis (HT) Study Section, NIH
- Vice Chair, Gordon Research Conference on Plasminogen Activation and Extracellular Proteolysis, Ventura, CA
Committee Service:
- Member, School of Medicine Council, University of Maryland Baltimore
- Member, Committee for Selecting UMSOM candidates for application of the HHMI GILLIAM FELLOWSHIPS for ADVANCED STUDY
- Director, REAP (Research and Engineering Apprenticeship Program)
Grants and Contracts
NIH/NINDS R01NS082607 (2013 - 2019): “Mac-1 coordinates PDGF-CC activation by microglia and promotes BBB opening”
AHA 18TPA34170550 (2018 - 2021): “A novel radiation-resistant CD11b-expressing leukocyte population with atheroprotective activities”
NIH/NHLBI R01HL142909 (2019 - 2023): “Targeting the Proinflammatory Activity of Integrin Mac-1 for Treatment of Atherosclerosis”
NIH/NINDS R01NS110630 (2019 - 2024): "Ligand-dependent and cell type-specific functions of integrin CD11b/CD18 in multiple sclerosis"
Lab Techniques and Equipment
- Various knockout, knockin and transgenic mice.
- Mouse models conducted in the laboratory:
- Atherosclerosis and restenosis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Ischemic stroke
- Bone repair and regeneration
- Collagen-induced Arthritis
- Immune tolerance
- Adoptive cell transfer and bone marrow transplantation.
- Laser scanning confocal fluorescence microscopy and FRET.
- Live cell imaging.
- Flow cytometry and FACS cell sorting
- RNAi, CRISPR, RNAseq, and single cell RNAseq.
- Protein expression in E.coli, Sf9 insect cells, HEK293 and RAW264 cells.
Laboratory Personnel
- Chunzhang Cao, PhD (Assistant Professor)
- Vishnuprabu Durairaj Pandian, PhD (Postdoctoral Fellow)
- Hongxia Chen, PhD (Postdoctoral Fellow)
Postdoctoral Fellow Positions Available
NIH-funded postdoctoral fellow positions are available to investigate the role of specific subsets of macrophages in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, as well as autoimmune diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. The major goal of these studies is to molecularly define how integrin receptors on inflammatory and resident macrophages differentially regulate intracellular signaling events and
thereby confer macrophages with either pro- or anti-inflammatory activities in the setting of health and diseases. The post-doc fellow will need to perform experiments involving vascular/macrophage biology, immune regulation, and murine models of human diseases. Prior experience in at least some of these methodologies, such as molecular biology, immunology, and transcriptomics/bioinformatics is preferred.
Please send letter of interest, your contact information, CV, and list of three references to Dr. Li Zhang at lizhang@som.umaryland.edu
